The explanation of the present lies in the properties of the past.
– Rebecca Cassidy, from “Arborescent Culture – Writing and Not Writing Racehorse Pedigrees”
Pedigrees have long been the backbone of genetics. Not surprisingly, therefore, we tend to think of pedigrees as primarily medical tools for analyzing inheritance patterns, assessing risk, and conducting research, as well an opportunity to elucidate the dynamics of family relationships. But pedigrees and the various other graphic, textual, and oral descriptions of family histories have played many roles over time and across cultures. These familial maps provide insight into the underlying and sometimes nefarious motives and goals of the mapmakers.
Here I propose 14 additional reasons family histories might be recorded, beyond clinical genetics. There is some overlap in these categories; the world has a tendency to not fit into neat and discrete categories. The Good Readers of The DNA Exchange might think of additional functions, and I encourage you to add your thoughts in the Comments section.
1. Curiosity About ”Blood Family”: Who were my ancestors? What were their lives like? How do they and their lives affect my life? Oral traditions of genealogy probably go back to the dawn of humanity. Starting around 4 centuries ago, as reading, writing, and education became more commonplace, the practice of recording a family history in graphic or text form started to become more commonplace. Think of the now largely forgotten tradition of The Family Bible, with its record of births. Or of folk art family trees with images of ancestors hanging from its branches. The widespread availability of relatively inexpensive DNA ancestry testing and online genealogical tools, along with genealogy-based TV shows like Finding Your Roots, has led to an explosion of interest in exploring and recording family histories. Of course, some people find out that “blood family” isn’t exactly who they thought it would be, which can disrupt familial relationships and lead to a whole host of complicated issues.

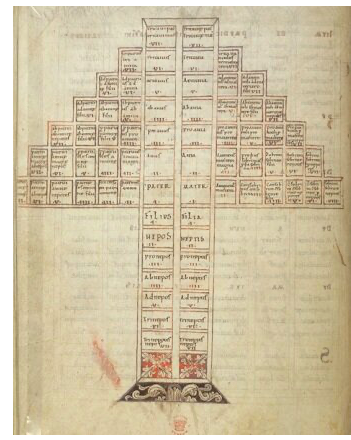
2. Political: Pedigrees have long been tied to establishing the hereditary legitimacy of royalty to rule over a people. Some scholars argue that the words king and kin are etymologically related, and the oldest etymological sense of the word queen seems to simply be “wife.” European genealogies, especially among Germanic peoples, were described prior to the 11th century but these were mostly succession lists of kings (often, but not always, father to first-born son) or attempts to trace ethnic origins to a mythological ancestor. One of the earliest surviving royal pedigrees is of the Carolingian Dynasty, created in the early 11th century, some 200 years after the death of Charlemagne. In various versions of this pedigree, relatives were added or subtracted to legitimize claims to rule some of the lands that emerged after the empire’s collapse.
Another example of a pedigree strategically including or omitting different people, and perhaps fictionalizing some relationships, can be found in John Hardyng’s 15th century rhyming verse Chronicle. Hardying (also spelled Harding) crafted a genealogy for Richard Duke of York and his descendants that managed to legitimize the entitlement of the House of York to the thrones of Britain, France, Portugal, and Spain. Oh, and Jerusalem too, for good measure. Hardying’s chronicle also attempted to de-legitimize earlier genealogical claims to the throne made by John of Gaunt, founder of the House of Lancaster. Hardyng’s Chronicle was propaganda that served as justification for The War of the Roses between these rival branches of the House of Plantagenet.
3. Religious: Genealogies have been used to establish divine lineages for religions. The so-called Tree of Jesse, which traces the ancestry of Jesus back to Jesse, the father of David, is a classic example of this, as are the Biblical Begats that trace the lineage of Adam to Noah. By the same token, Islamic genealogy traces the Prophet Muhammad back to Abraham and Adam.
Medieval monastic orders, particularly the Franciscans and Dominicans, created monastic “family trees” (called Ordensstammbäume) with a founder at its root and various prominent members of the order branching off the tree, evoking the sense of the monastic community as a kind of family.

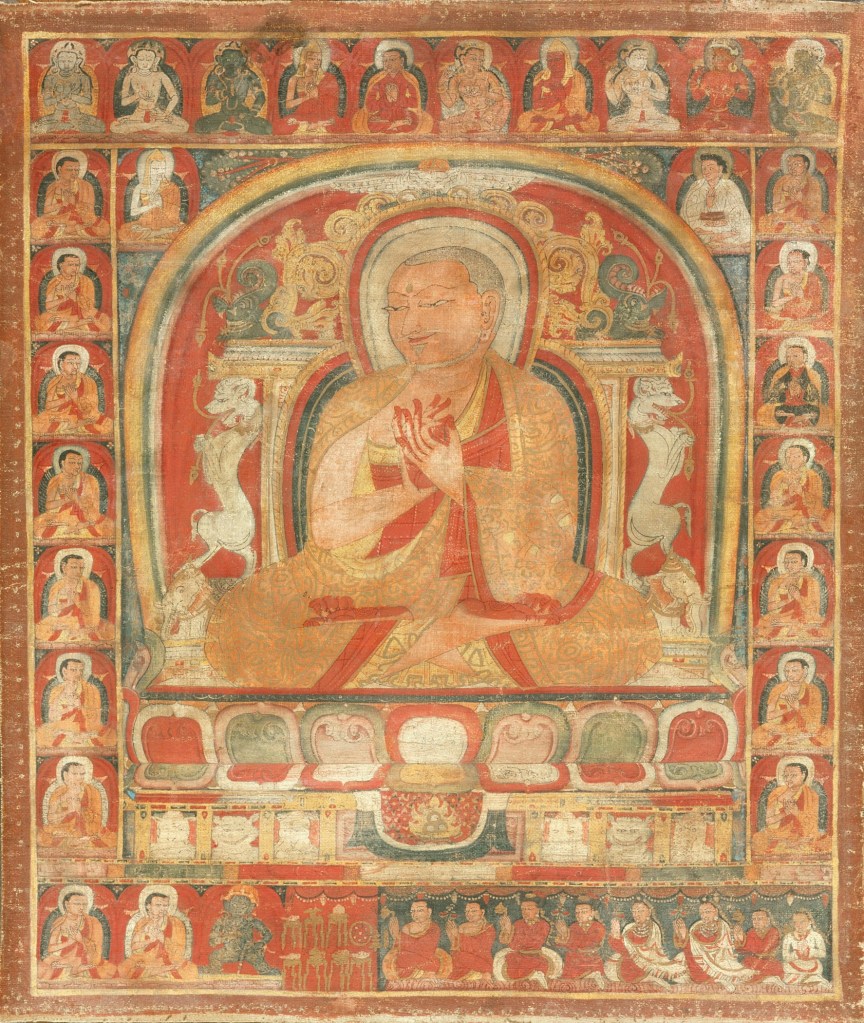
Some rulers traced their ancestry back to gods to legitimize their right to rule – Caesar Augustus claimed to be descended from Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Juno; the Pharaohs claimed to be descended from Ra, the God of the Sun, Sky, and other domains. The 13th century Secret History of the Mongols, based on earlier oral and written works, detailed the partially mythological ancestry of Genghis Khan. Tibetan Buddhism incorporates spiritual genealogy into its practice, based on lineages of teachers and their pupils, their pupils’ pupils, and so on. Tibetan Buddhism also uses reincarnation lineages (who gets reborn as whom) to determine religious leaders and, ultimately, the Dalai Lama as a political and religious leader.

Puritans believed that the books that will be opened on Judgment Day would contain genealogies, most notably “a register of the genealogies of New England’s sons and daughters.” In the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-Day Saints, genealogy is critical in identifying those ancestors who died before the revelations of the Book of Mormon and who therefore need to be baptized. Posthumous baptism allows these ancestors to enter Heaven and also serves to strengthen eternal family bonds.
4. Legal: One of the oldest reasons for formally recording a family history was to determine the appropriate inheritance of land and property. The Roman legal text Pauli Sententiae (tr., “The Opinions of Julius Paulis”) from around 300 CE states that determining who is entitled to inherited property involves drawing up stemmata (s., stemma; essentially a form of a pedigree): “The stemmata of cognate relationships are separated by a straight line into two lines, one of which represents the ascendant and one the descendant. From the ascendant are horizontal lines starting at the second degree.”
It was also within the legal system that the word “pedigree” was first coined, in Norman-English legal documents. The word “pedigree” is actually a product of the Anglo-Norman dialect of England and did not enter “mainstream” French until the 1820s.
More recently, and more controversially, forensic genealogy has used DNA from commercial ancestry testing companies to re-construct pedigrees to identify potential perpetrators of crimes.
5. Establishing The Right to Be Assigned a Specific Coat of Arms: Coats of arms evolved from the designs on the chain mail armor of medieval knights, starting around the 12th century. The right to display a specific coat-of-arms is determined by who your ancestors are, and are assigned by a central authority, such as England’s College of Arms. Applicants for a coat must register “a pedigree showing direct male line descent from an ancestor already appearing therein as entitled to arms” with the College, which then verifies the information.

6. Ontological: Genealogies help establish a framework of reality and an individual’s relationship to the world about them. These genealogies incorporate the physical and metaphysical world. Genetic relationships may be secondary or irrelevant to such genealogies. For example, the Nekgini-speaking people of Papua New Guinea live in small villages called palems. Siblings are defined as all members of the second generation that have lived in the same palem, regardless of genetic relationship. They are considered siblings because they have a shared knowledge of the land, spirits, and food particular to their palem.
Many Native American people trace their clans – and thus to some extent their families – back to creation stories that tell how the first people came into being, sometimes from the biological realm and sometimes from the physical realm. Clan names were often derived from the animal or plant from which the clan is descended
7. Anthropological Studies of Kinship: Starting in the late 19th century, and extending well into the 20th century, kinship analysis formed a core part of ethnographic studies of what were viewed as “primitive cultures” (typically in countries that had been colonized by Western Europeans). Classic studies in the tradition of Lewis Henry Morgan, W.H.R. Rivers, and E.E. Evans-Pritchard typically imposed their Western view that genetic relationships universally formed the basis of kinship, which was often at odds with how the societies they were studying viewed kinship. Indeed, anthropologists often complained of the difficulty of trying to overlay English kinship terms and relations onto native systems and terminologies. Not every culture views relationships in terms of a branching genetic tree or genetic ancestors.
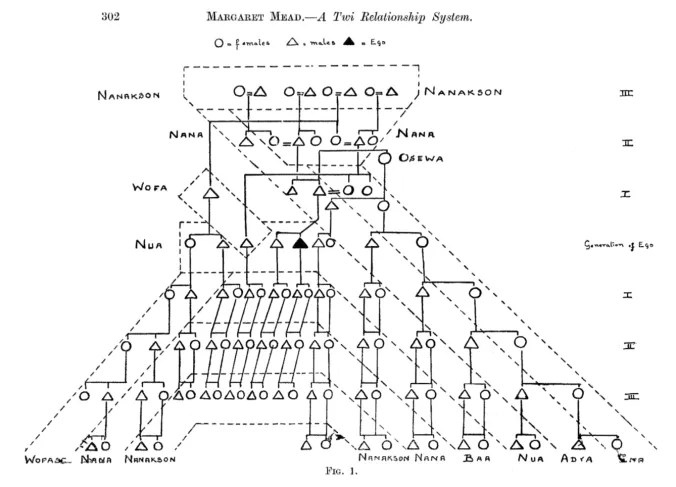
As an interesting aside, in classic anthropological pedigrees males were sometimes depicted with triangles rather than the squares characteristic of genetics-based pedigrees. This may just reflect a difference of tradition, but one could speculate that it was a conscious attempt to distance anthropology from eugenics. The image below is Margaret Mead’s pedigree of the kinship relationship system of the West African Twi from 1925 (but not published until 1937), probably just before she left to start her (in)famous fieldwork in Samoa. It is one of the earliest anthropological pedigrees to use symbols to denote people. It was drawn at Columbia University where she was a graduate student studying with Franz Boas, a founding figure of anthropology and one of the most vocal critics of eugenics. So it’s not out of the question that the triangle male could conceivably be a nose-thumb at eugenics, though I am unaware of hard evidence to support this contention. Mead’s kinship pedigree, by the way, was based on information provided by Ansa, another student at Columbia University who gave his address as Kwadjowusu, via Apegusu, Gold Coast. The text around the edges indicate the name of that relationship rather than the name of that individual, e.g., nana = any grandparent (funny how some words like nana seem almost universal). Twi relationship terms can vary with whether the speaker is a man or a woman.
8. Mate Choice: Many societies impose rules on who one can or cannot marry or have sexual relations with, dependent on the relationship between the two people. Indeed, “incest taboos” exist in virtually every society, though with different criteria as to what constitutes an incestuous or inappropriate relationship (not always limited to genetic relatives). In Western Europe where, for reasons that are not entirely clear, the Catholic Church tightly regulated marriage to genetic relatives to an astounding degree of relatedness (but also regularly granted exceptions when it was politically or economically expedient). A couple, usually royal or aristocratic, who wished to be married would submit their pedigrees to the Church, which would decide whether the union was acceptable according to relationships established by an arbor consanguinitatis, a table that laid out the degree of genetic relationship between various family members.
9. Ego Gratification and Social Status: People often search their family history in hopes of finding a Genghis Khan or a Charlemagne (statistically, it’s relatively likely that everyone has a famous ancestor). Americans like to find a relative who was one of the 100 or so people who “came over on The Mayflower,” and many Aussies find a certain pride in being descended from a transported convict. Somehow it makes you feel just that much more special.
Ancestry-based social organizations can provide a sense of shared ideology and elite status – and perhaps a distorted sense of patriotism. Membership in the Daughters of the American Revolution (DAR) is available to “[a]ny woman 18 years or older who can prove lineal, bloodline descent from an ancestor who aided in achieving American independence is eligible to join the DAR. She must provide documentation for each statement of birth, marriage and death, as well as of the Revolutionary War service of her Patriot ancestor.” Likewise, membership in the United Daughters of the Confederacy and the Sons of Confederate Veterans require an ancestor who fought for The Confederacy during the American Civil War. Members see themselves as socially privileged, based on a shared ancestry, racist ideology and false narratives about slavery and the Civil War.
10. Tools of Oppression and Conformity: As I’ve written about previously in this space, pedigrees have been used to oppress people, as happened with the American (and other) Eugenics Movements. Pedigrees could be the basis of life and death in Nazi Germany, when any Jewish ancestry could have tragic consequences. Pedigree symbols have also typically forced people into one of two genders, male or female.
11. Social Organization: Genealogy can serve as a basis for organizing social structure and social interactions. In the late 7th and early 8th century, Hishām ibn al-Kalbī authored a comprehensive and massive genealogy called Jamharat al-nasab (“The Multitude of Genealogy”) that amassed ~35,000 names and included the paternal lineages of most of the Arabian peninsula. al-Kalbi’s genealogy organized the various Bedouin tribes of the area and traced them to two ancestors, Qahtan (Noah’s great-great grandson) for the southern tribes, and Adnan, a descendant of Abraham, for the northern tribes. Arab genealogy, (nasab in Arabic), served to structure social relationships – who owed allegiance to whom, who had elite status based on being a Sayyid or direct descendant of Muhammad through his daughter Fatimah (all 3 of the Prophet’s sons died young), potential marriage partners, who could be a sheikh, and in the organizing of the diwan (networks through which money and other goods were distributed). There is reason to believe that al-Kalbī may have created some fictitious relationships and down-played the importance of some tribes, perhaps for political purposes.
Interestingly, in the early Arabic Medieval period, the human body, rather than a tree, served as a metaphor for genealogical relationships, with various parts of the body representing different segments of ancestry, starting with an entire ethnic group at the top of skull and proceeding on down to the extended family at tip of the lower extremity.
12. Describing Family Dynamics: Social Work and Psychotherapy have an equivalent to a pedigree called a genogram. A genogram looks just like a genetics pedigree but uses a variety of graphic lines that connect individuals to one another to indicate their emotional relationships (e.g., Very Close, Estranged, Sexual Abuse).

Genetic Counseling has a similar but infrequently used tool called the Colored Eco-Genetic Relationship Map (CEGRM), developed by genetic counselors Regina Kenen and June Peters in 2001. According to its authors, the CEGRM “… combines information that can be derived from pedigrees, genograms, ecomaps, and social network analysis in a single, or series of, pictorial maps based on colors and shapes. The CEGRM is based on a social systems perspective, particularly emphasizing social exchange and resource theories.”
13. Poetry/Literature: There is a very old tradition of establishing the mytho-historical origins of characters in epic poems. The genealogy at the beginning of The Iliad links the lineage of the Greek Gods to humans and to the natural world. The opening verses of the Indian epic Bhagavid Gita, which describes a battle between the armies of two cousins, lay out the familial links among various warriors on both sides. In addition to its deep spiritual messages, this epic examines the internecine and senseless nature of intra-familial conflict.
Teachers, fathers, sons, grandfathers, maternal uncles, grandsons, fathers-in-law, grand-nephews, brothers-in-law, and other kinsmen are present here, staking their lives and riches. O Madhusudan, I do not wish to slay them, even if they attack me. If we kill the sons of Dhritarashtra, what satisfaction will we derive from the dominion over the three worlds, what to speak of this Earth?
– From the opening verses of the Bhadavid Gita
In more recent times, many novels structure their narrative around the stories of multiple generations of a family, like Thomas Mann’s Buddenbrooks, Gabriel García Márquez’s One Hundred Years of Solitude, and Min Jin Lee’s Pachinko, to name but a few.
14. Dehumanization By Erasing Genealogies: Just as important as the functions of the existence of a pedigree is the absence and intentional obliteration of a genealogy. Slavery, especially in the Americas, resulted in the tearing apart of families. This started in their native lands, where families were often separated when people were forced into enslavement. Then, in the lands they were forcibly transported to, parents, children, and siblings could be further torn asunder when they were sold to different plantations, often with indifference to the family structure. Enslaved people could not be taught to read or write under pain of the lash or worse, so they could not even record their genealogy to try to maintain a record of their fractured families. Enslaved people were considered legally nameless until they were sold and some slave owners freely named their human property. Government censuses and wills often did not even give the dignity of recording names, or even just first names, of enslaved people.
The absence of a name along with eradicating a family’s genealogy were powerful ways to rob people of the essence of their humanity. If enslaved people had no humanity, then you can justify enslaving them and depriving them of any rights. They are no better than property or animals (though antebellum “gentlemen” were careful to record the pedigrees of their race horses).

Federal Slave Census Schedule, Warren County Mississippi, 1860. Only a few names of enslaved people are recorded. Image from The National Archives, https://www.archives.gov/files/calendar/genealogy-fair/2018/2-kluskens-presentation.pdf
Family histories help societies and people make sense of their lives and the world they live in by telling a particular story. Every family history is a family story. But every story has a reason it is being told, one that determines the cast of characters, why they are included, and why some characters are left out. Some stories are noble, some mundane, some medical, some political, and some are religious. The darkest stories are those that oppress and those that cannot be told because they have been destroyed, taking with it the soul of a people.
________________________________________________
For additional postings about pedigrees, see:
https://thednaexchange.com/2011/12/04/the-implicit-judeo-christian-ethic-of-pedigree-nomenclature/
https://thednaexchange.com/2023/01/03/no-quibbling-over-sibling-sisters-and-brothers-we-are-one/


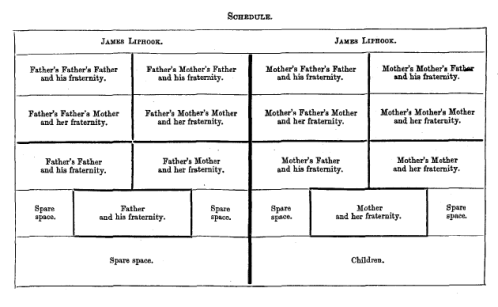

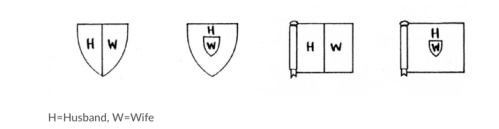






 I have resisted using family history questionnaires because for most patients those questionnaires probably just feel like homework assignments. Besides, I am not convinced that questionnaires really save much clinic time. More critically, the process of constructing a pedigree provides great insight into a patient’s understanding of genetics, disease, and family dynamics. And, truth be told, a questionnaire lacks a pedigree’s minimalist elegance and concise pictorial encapsulation of complex information.
I have resisted using family history questionnaires because for most patients those questionnaires probably just feel like homework assignments. Besides, I am not convinced that questionnaires really save much clinic time. More critically, the process of constructing a pedigree provides great insight into a patient’s understanding of genetics, disease, and family dynamics. And, truth be told, a questionnaire lacks a pedigree’s minimalist elegance and concise pictorial encapsulation of complex information.